Since November 9, several laboratories have announced the development of a vaccine that is more than 90% effective. Pfizer-BioNtech laboratories present their first results obtained on a messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine.
What is the principle of this vaccine? What impact on its cold chain ?
Historical vaccines with infectious agents
Historically, the first vaccines were designed from the infectious agent. These early vaccines contain either the whole virus attenuated by physical or chemical treatment, or a modified virus incapable of multiplying. The injection of these « harmless » infectious agents stimulates the immune system, which then learns to eliminate the pathogen by producing antibodies. This type of vaccine requires the cultivation of large quantities of pathogens. The storage of these vaccines is mainly between 2 ° and 8 ° C.
Vaccines without infectious agents, resulting from genetic engineering
In the case of the messenger RNA vaccine, the laboratories inoculate a small fragment of a genetic sequence of the virus into a human cell. This little piece of messenger RNA carries the code to make Spike proteins, the protein on the surface of the virus that allows it to adhere to cells. Spike is then detected by our immune system which reacts by producing antibodies. This vaccine technique is faster to set up because it is not necessary to cultivate large amounts of pathogenic virus. The vaccine is also less toxic because there is no pathogen to inoculate. However, RNA is an extremely fragile molecule that must be stored at very low temperatures: below 80 degrees Celsius. The cold chain must be strict so as not to denature the vaccine.
The SPIKE proteins on the surface of the COVID 19 coronavirus, the source of the messenger RNA vaccine.
How to store and transport the COVID 19 vaccine at a temperature below -80 ° C ?
Super-freezers, a very advanced technology

Traditional vaccines can be stored between 2 ° C and 8 ° C and can therefore be stored in a conventional refrigerator. In the case of the COVID 19 vaccine, it is about keeping the temperature below -80 ° C. “Super-freezers”, using compressors and specific refrigerant gases, make it possible to go down in several stages to -86 ° C. But these “super-freezers” are not frequent and remain at a fixed position. Refrigerating entire trucks is too restrictive and dangerous for transporters because at -80 ° C our members freeze in a few minutes.
An easier solution is to store COVID 19 vaccines in contact with liquid nitrogen or in contact with dry ice.
Dry ice as a refrigerant for messenger RNA vaccines
Dry ice, a material at -78.9 ° C
Dry ice is a material which, at atmospheric pressure, passes directly from a solid state to a gas state without passing through the liquid phase. This phenomenon is called sublimation. Ice turns directly into gas at a temperature of -78.9 ° C without leaving a trace. It simply means that dry ice “disappears” as it heats up, leaving no residue or waste to clean up. From a thermal point of view, sublimation cools its environment very effectively.
Combine an insulated container with dry ice to transport vaccines at -80 ° C
To transport pharmaceutical products at a temperature below -80 ° C, one solution is to combine an insulated container with dry ice. The insulated container will slow down the heat ingress while confining the cold when the dry ice will maintain the temperature stability at -80 ° C. Remember that with sufficiently isothermal containers, the holding time at a temperature of -80 ° C can last up to 120 hours. The density of 1.5 kg / m3 of dry ice is advantageous: dry ice takes up little space.
Packing and labelling
Biological products such as vaccines are not subject to specific transport regulations. However, when transported under snow or dry ice, specific packaging and labeling instructions need to be applied:
- Packages and containers containing dry ice must be able to withstand the very low temperatures of dry ice without being altered or significantly weakened ;
- Packages and containers must be designed and manufactured in such a way as to allow gas to escape in order to prevent a rise in pressure which could lead to packaging rupture;
- The biological products transported must be wedged with linings or supports to prevent any movement of biological materials in the container once the dry ice has been dissipated ;
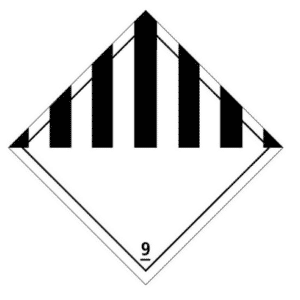
- Dry ice is classified as dangerous goods of class 9: “Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles” under UN number 1845. A This title, the transport container must bear the risk label opposite, indicating the designation o ffficial “Dry ice” or “Carbon dioxide, solid” followed by the words “As coolant”. These marks must be durable, legible and placed in such a location and be of such a size in relation to the package that they are easily visible.
For example, the CarryTemp and Diagnocase insulated containers from COLD & Co have been designed to provide packaging and transport of organic products under dry ice. The temperature of -80 ° C can be maintained for up to 4 days.
Please contact us for more information on this !